
On the other hand, incremental costs are future costs that are directly influenced by the decision at hand. When analyzing different options, businesses should focus on incremental costs rather than sunk costs to make rational and forward-looking decisions. The term incremental cost refers to the cost that the business incurs for producing an extra unit. The calculation of incremental cost shows a change in costs as production expands.
- So instead of taking one hour to make two products, your employee can do it in 45 minutes.
- In other words, incremental costs are solely dependent on production volume.
- Remember, identifying relevant costs requires a holistic approach, considering both short-term and long-term implications.
- The incremental cost is the cost involved to make an additional unit of product.
- Incremental cost refers to the change in total cost that occurs as a result of producing or consuming one additional unit of a good or service.
Incremental Costs
The cost of each additional unit will be different, and the company must weigh the pros and cons of each option to decide which is best. To increase production by one more unit, it may be required to incur capital expenditure, such as plant, machinery, and fixtures and fittings. A restaurant with a capacity of twenty-five people, as per local regulations, needs to incur construction costs to increase capacity for one additional person. In summary, incremental cost isn’t a mere line item on a balance sheet; it’s a compass guiding us through the labyrinth of choices.

Understanding Incremental Cost
Whether you’re optimizing business processes, designing public policies, or improving patient care, understanding incremental costs empowers you to navigate complex choices effectively. The incremental cost is the cost involved to make an additional unit of product. That also means the additional cost incurred by a company if it produces one extra unit of output.
Key Takeaways
The importance of each factor may vary depending on the specific context and goals of the decision-maker. By carefully considering all relevant aspects and using appropriate analytical tools, you can make well-informed decisions that align with your objectives. Incremental costs are also used in the management decision to make or buy a product. Some custom products might not be readily available for the business to buy, so the business has to go through the process of custom ordering it or making it. Incremental analysis models include only relevant costs, and typically these costs are broken into variable costs and fixed costs. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of incremental cost empowers businesses to make well-informed decisions that can positively impact their bottom line.
Incremental Cost Formula
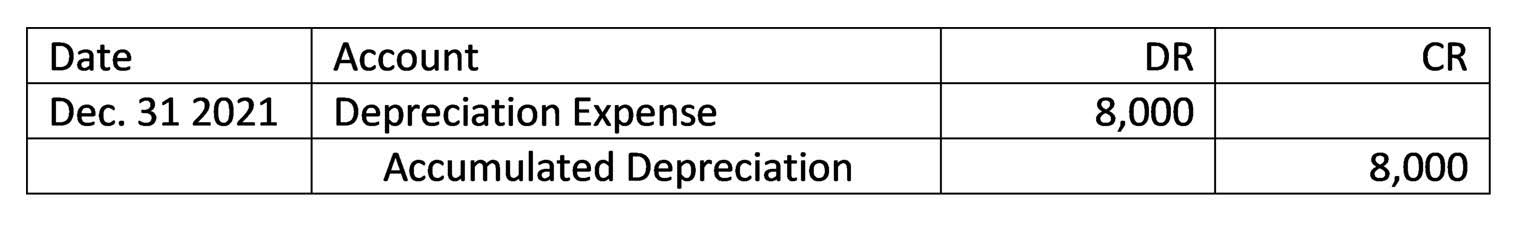
Incremental analysis provides a structured framework for https://www.facebook.com/BooksTimeInc/ decision-making. By focusing on the changes brought about by a specific choice, managers can evaluate options objectively. Whether it’s a small operational decision or a major strategic move, incremental analysis helps navigate the complexities of business with clarity and precision. Remember, the devil is in the details, and incremental analysis helps uncover those crucial details that drive smart decisions.
What Is Incremental Cost?
- You estimate that you would sell 2 million widgets in the first year after expanding.
- By comparing the additional costs incurred with the additional revenue generated, businesses can assess whether the venture is financially viable.
- Below are the current production levels, as well as the added costs of the additional units.
- At its core, incremental cost of capital refers to a single unit that a company must raise.
- The incremental volume change is how much extra output is being proposed or considered for evaluation.
- If we look at our above example, the primary user is product ‘X’ which was already being manufactured at the plant and utilizing the machinery and equipment.
Incremental costs are also useful for deciding whether to manufacture a good or purchase it elsewhere. Understanding the additional costs of increasing production of a good is helpful when determining the retail price of the product. Companies look to analyze the incremental costs of production to maximize production levels and profitability. Only the relevant incremental costs that can be directly tied to the business segment are considered when evaluating the profitability of a business segment.

Benefits to Incremental Cost Analysis
Forecast LRIC is evident on the income statement where revenues, cost of goods sold, and operational expenses will be affected, which impacts the overall long-term profitability of the company. When a factory considers installing pollution control equipment, incremental cost the incremental cost may seem high. However, the long-term benefit—cleaner air, healthier communities—justifies the investment. Suppose a software company is considering adding a new feature to its product.
What is Incremental Cost?
Also, fixed costs can be difficult to attribute to any one business segment. From a managerial perspective, incremental costing provides valuable insights into the cost-effectiveness of different options. It helps businesses identify the additional costs incurred and the corresponding benefits gained by choosing one option over another. This analysis enables decision-makers to https://www.bookstime.com/articles/reversing-entries allocate resources efficiently and optimize their financial outcomes. Understanding the concept of incremental cost is crucial for decision making and cost-benefit analysis. Incremental cost refers to the change in total cost resulting from a specific decision or action.